How To Build A Load Planning Software In 2025: Features, Cost, Steps, & More
Keyur Patel
September 12, 2025
31 min
Imagine a logistics operation where every shipment is precisely packed, trucks leave the dock fully utilized, and last-minute changes are handled without panic or paperwork. Now, picture all of that happening without relying on complex spreadsheets or outdated manual planning.
That is not a futuristic fantasy. It is what savvy businesses are already doing in 2025.
You will be surprised to know that the Load Planning Services & Solutions Market is projected to reach nearly US$ 1555.7 million by 2029, demonstrating a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 6.5% during the forecast period.
The global logistics and freight industries are undergoing a digital shift. Tight delivery schedules, volatile shipping costs, and increasing sustainability demands push companies to rethink how they plan, load, and deliver goods.
Manual methods are no longer efficient or growth-friendly. In this high-stakes environment, load planning software has become the backbone of streamlined shipping and operational intelligence.
Wondering what it is?
Continue reading to learn what load planning software actually does, how it differs from load optimization tools, which features matter in 2025, and how to build a scalable solution that fits your business goals. We will also cover custom software development costs, integration best practices, and real-world applications.
We have curated this guide for decision-makers, founders, product managers, logistics professionals, and software leaders who want to transform their freight planning.
Let’s get started!
Introduction To The Load Planning Software Landscape
Load planning software has become mission-critical for logistics, trucking, manufacturing, and freight-forwarding industries.
Whether you’re shipping locally or managing global routes, the ability to optimize space, lower fuel consumption, and abide by load regulations directly affects your bottom line. In 2025, this is not just about saving costs; it is about staying competitive.
Why Logistics, Trucking, And Manufacturing Industries Need Load Planning Software
These industries deal with complex challenges every day. Truckload inefficiencies, underutilized fleet capacity, and manual load distribution often lead to delayed deliveries and unnecessary costs.
Truckload planning software and freight planning tools solve these issues by providing real-time load configuration, optimal routing, and superior visibility across supply chains.
Manufacturers use custom load planning solutions to reduce material waste and maximize outbound shipping. Aircraft load planning software ensures safety and balance across air cargo shipments.
Every segment of transportation benefits from having purpose-built load planner software that works in sync with its operational needs.
Why 2025 Is The Right Time To Invest In Load Planning Software
Three major shifts are driving adoption:
- Automation is no longer optional. Load planning and optimization software powered by AI can perform tasks in seconds, which once took hours manually.
- Sustainability regulations are tightening. Efficient load planning lowers carbon emissions and aligns with global compliance efforts.
- Cloud infrastructure is now mature. Cloud-based load planning software allows teams to access plans from anywhere, collaborate in real-time, and scale easily.
For transportation management software to work seamlessly, load planning tools need to integrate with fleet management software, GPS tracking systems, and logistics data hubs. It is precisely where modern shipping logistics software is making its mark.
2025 is not the time to wait and see. It is the moment to lead with savvy systems, better visibility, and fully optimized loads.
What Is Load Planning Software, And Why Does It Matter
Load planning software is a digital tool that helps logistics teams arrange shipments within a vehicle or container in the most systematic way possible. This includes positioning freight based on weight, size, type, and destination while also accounting for regulations and safety requirements.
Whether it is truckload planning, aircraft load planning software, or solutions for sea freight, the goal is always the same: maximize space, reduce costs, and ensure safe delivery.
Load Planning vs. Manual Planning: What’s More Cost-Effective In 2025?
Manual planning often leads to misjudged space, unbalanced loads, or regulatory violations. It takes time, leaves room for error, and cannot adapt quickly to last-minute changes.
In contrast, load planner software uses algorithms and intelligent logic to:
- Automate weight and space distribution
- Visualize the load configuration
- Adjust dynamically to cargo changes
- Integrate with route optimization software
By combining these capabilities, modern load optimization software boosts operational efficiency across the board.
Real-Life Use Cases In Trucking, Warehousing, And Manufacturing
- Trucking fleets use truckload planning software to reduce the number of trips needed, saving fuel and time.
- Manufacturers rely on logistics software development to create custom load planning solutions for precise delivery schedules.
- Warehouses and distribution centers benefit from integrated transportation management software that ensures cargo is prepared, tracked, and shipped without delays.
➡️ In 2025, load planning is foundational for any logistics or freight operation that wants to run smarter, faster, and leaner.
Load Planning vs. Load Optimization Software: Key Differences And Synergies
While often used interchangeably, load planning software and load optimization software serve different roles in the logistics chain. Understanding how they differ and work in tandem can help businesses choose or build the right tool.
What’s The Difference?
- Load Planning Software focuses on how freight is physically arranged in containers, trailers, or cargo holds. It handles dimensions, stacking rules, safety guidelines, and weight distribution.
- Load Optimization Software goes a step further by determining the most cost-efficient way to transport goods. It considers delivery routes, shipment consolidation, fuel consumption, and deadlines.
In short, planning is about packing cleverly. Optimization is about doing it profitably.
Where They Overlap
Modern transportation management software often includes both load planning and optimization features. These systems:
- Select the right vehicle based on load type
- Suggest optimal load distribution based on route and delivery times
- Integrate with fleet management software for real-time tracking and updates
This synergy makes logistics software development highly valuable when creating custom load planning solutions that adapt to complex business needs.
When To Use One or Both
- Use load planning alone if your primary goal is to ensure cargo safety and vehicle balance.
- Use optimization alone if you already have basic planning capabilities but want to cut costs or increase speed.
- Use both for enterprise-level freight planning software that needs to scale across fleets and warehouses.
A Visual Glance At Side-by-Side Comparison
| Criteria | Load Planning Software | Load Optimization Software |
| Primary Focus | Physical arrangement of cargo | Efficient and cost-effective delivery strategies |
| Key Functions | Load modeling, dimension fit, stacking rules | Route planning, shipment consolidation, and cost reduction |
| Ideal For | Ensuring safety, space utilization, and compliance | Reducing fuel, time, and delivery costs |
| Output | Loading diagrams or visual plans | Optimized route and shipment schedules |
| Tech Integration | Often linked with warehouse or packaging systems | Often linked with fleet and transportation management systems |
| Use Case Example | Stacking pallets in a trailer without exceeding the axle weight | Planning the shortest multi-stop delivery routes for perishable goods |
| Best For | Truckload planning, aircraft load planning, and cargo safety | Route optimization software, freight cost savings |
| Combined in TMS? | Frequently combined with optimization in logistics software | Frequently combined with planning in enterprise tools |
Together, these tools give logistics teams a comprehensive picture. They ensure shipments are not only packed correctly but also move through the supply chain with maximum efficacy.
In a Nutshell: Load planning software ensures your cargo fits safely and systematically, while load optimization software finds the most innovative and cost-effective route. Using both delivers the best of physical planning and strategic execution.
How Load Planning Software Works
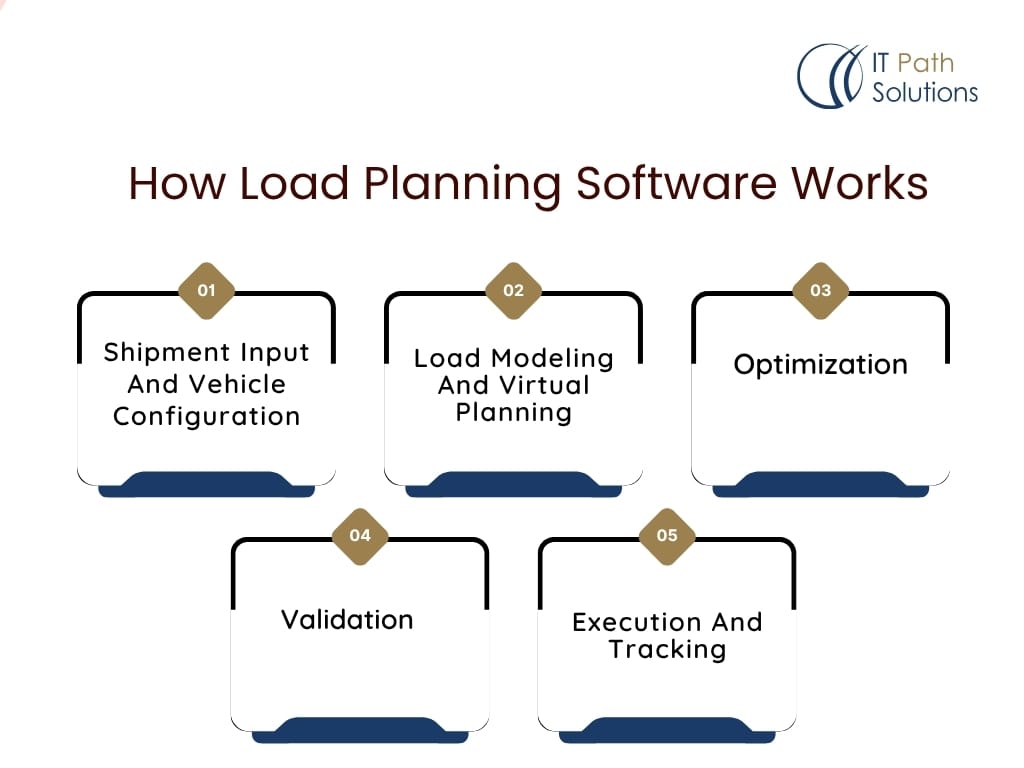
Load planning software operates like a digital logistics brain. It takes in the raw data of what needs to be moved, where it needs to go, and what it’s being transported in, then transforms that into a plan that saves time, space, and fuel. Let’s break it down step by step.
Step 1: Shipment Input And Vehicle Configuration
Users begin by entering detailed shipment information. It includes package dimensions, weights, contents, stacking restrictions, and destination details. Simultaneously, they input vehicle specifications such as trailer type, cargo capacity, axle limits, and load-bearing surfaces.
Step 2: Load Modeling And Virtual Planning
The system then creates a virtual 2D or 3D load plan. This model visually represents how cargo will be arranged inside the truck, container, or cargo hold. The software ensures packages fit within the vehicle’s space while adhering to legal, weight, and balance limits.
Step 3: Optimization
Using built-in algorithms or AI engines, the software rearranges loads for space optimization and stability. It considers constraints like fragile items, stacking order, and center of gravity. Some platforms blend this with fuel and route scheduling for added efficiency.
Step 4: Validation
The plan is validated against safety rules, weight distribution guidelines, and transportation regulations. If it fails to meet any requirement, the system flags the issue for manual review or suggests alternatives.
Step 5: Execution And Tracking
Once approved, the load plan is pushed to logistics teams or integrated into transportation management software. With connected systems, dispatchers and drivers can access load details, and managers can track execution in real-time.
Smart Summary: Modern load planning software transforms cargo input into a savvy, visual plan, guiding every step from loading the dock to the destination. It enhances accuracy, saves resources, and reduces costly mistakes in logistics execution.
Must-Have Features of Modern Load Planning Software
Today’s logistics challenges demand more than just manual planning or basic spreadsheets. The best load planning tools are equipped with robust features that automate, optimize, and streamline cargo planning.
Whether you’re running a freight company, a warehouse, or a large manufacturing operation, the appropriate set of features can make or break your efficiency.
Let’s look at the essential features you should expect from powerful load planner software.
Core Features
These are foundational capabilities that every load planning software must include to handle the basic intricacies of transportation logistics.
| Feature | What It Does |
| Load Calculation Engine | Calculates weight, volume, and balance points based on cargo and vehicle data. Helps prevent overloading and ensures legal compliance. |
| Drag-and-Drop Load Interface | Provides an intuitive way to visually arrange cargo. Users can adjust load placements in a simulated environment. |
| Vehicle Dimension Matching | Matches cargo with compatible vehicles by evaluating dimensions, axle limits, and trailer types. |
| Compliance Tools | Flags violations related to axle weight, stacking restrictions, or safety standards. Offers instant alerts before execution. |
Advanced Features
Modern logistics operations need more than just the fundamentals. Here’s where high-end load optimization software takes it further.
| Feature | What It Does |
| AI-Powered Optimization | Uses machine learning to recommend efficient loading patterns that save time, reduce empty space, and cut fuel costs. |
| 3D Visualization | Offers a three-dimensional view of the load plan for better clarity, especially for irregular-shaped cargo. |
| Real-Time GPS Integration | Syncs with fleet management software to monitor vehicle movement and track cargo during transit. |
| Route and Fuel Cost Optimization | Suggests routes that align with load configuration and reduce travel distance and fuel usage. |
| Cloud Support and Mobile Access | Allows users to manage, update, and share load plans from anywhere through smartphones or web browsers. Great for teams on the move. |
Quick Recap: A well-rounded load planning system blends core logistics functionality with intelligent optimization. From visual planning to real-time GPS sync, every feature should aim to simplify your workflow, increase delivery accuracy, and reduce transportation costs.
Types Of Load Planning Software For Different Businesses
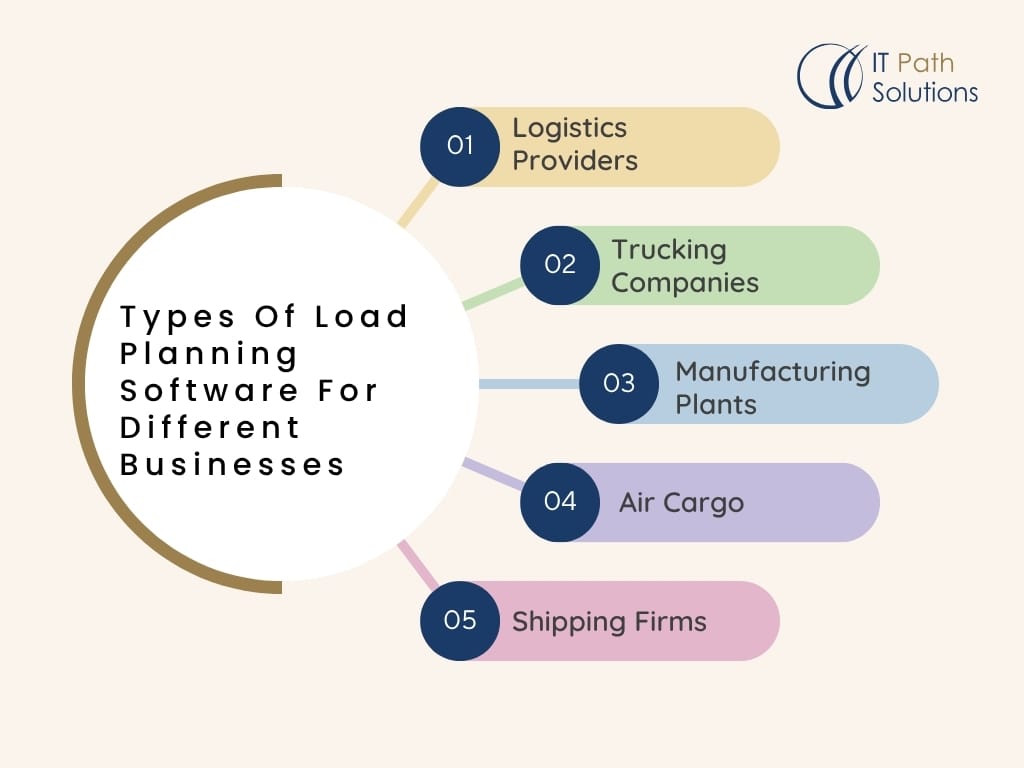
Not all cargo is created equal, and neither is the software that manages it. Your choice of load planning software should be precise, depending on the industry you operate in, your transportation needs, and the complexity of your cargo types. From trucking companies to global manufacturers, there is no one-size-fits-all solution.
Let’s explore the different types of load planner software and how they serve various industries and operations.
By Industry Use Case
| Business Type | Recommended Software Focus |
| Logistics Providers | Real-time route optimization, 3D load visualization, GPS tracking, and integration with TMS or ERP systems. |
| Trucking Companies | Truckload planning software that supports axle load calculation, driver route preferences, trailer matching, and compliance management. |
| Manufacturing Plants | Integration with WMS and production lines, pallet-based stacking optimization, and batch shipment planning. |
| Air Cargo & Shipping Firms | Aircraft load planning software and load planning software for air cargo with strict weight distribution, center of gravity calculations, and aviation compliance. |
By Deployment Model
| Model | Best For | Pros |
| SaaS-Based Software | Small to mid-sized logistics operations | Easy to deploy, scalable, cloud-accessible, and low upfront cost |
| On-Premise Software | Enterprises with custom security or data control needs | Total control over the system and data, better offline stability |
| Open Source Load Planning Software | Tech-savvy teams or startups with in-house dev support | Flexible customization, cost-effective, and access to community-driven upgrades |
By Freight Type
| Freight Category | Ideal Software |
| Full Truckload (FTL) or Full Container Load (FCL) | Load optimization software that maximizes vehicle fill rate and delivery efficiency |
| Less Than Truckload (LTL) or Less Than Container Load (LCL) | Load planning software with consolidation logic, cargo grouping, and split-delivery scheduling |
What You Should Know: The best load planning software is the one that aligns with your operational scale, freight complexity, and industry-specific needs. Whether you’re shipping across states or continents, selecting the ideal software type ensures smoother logistics and maximum cost efficiency.
Custom Load Planning Software Development
Off-the-shelf tools can only take you so far. When your logistics needs go beyond the basics, custom load planning solutions offer unmatched flexibility, control, and scalability.
Whether you manage an enterprise fleet, a manufacturing plant with complex shipment rules, or a freight brokerage firm that needs tighter system integration, developing your load planner software might be the wiser move.
When To Build Instead Of Buy
- Custom software development is not for everyone. However, it becomes crucial when:
- Your operations require specific logic not available in ready-made tools
- You need to integrate deeply with in-house systems like ERP, WMS, or TMS
- Off-the-shelf software fails to handle scale, edge cases, or unique cargo types
- Your workflows demand a custom-made user interface and automation rules
If you find yourself constantly tweaking your current system, using workarounds, or relying on spreadsheets to fill gaps, it’s probably time to consider going custom.
How To Build A Load Planning Tool From Scratch
Building load planning software from the ground up involves strategic thinking, clear business goals, and a development roadmap. Here is a brief overview of how to develop load planning software that works for your operation:
- Define the core requirements based on your freight type, user workflows, and compliance needs.
- Design a system architecture that supports real-time planning, optimization algorithms, and future upgrades.
- Develop the MVP with must-have features like drag-and-drop load modeling, vehicle matching, and compliance checks.
- Add advanced features like AI-based optimization, GPS tracking integration, and mobile-friendly dashboards.
- Test with real shipment data to validate the load recommendations and system accuracy.
- Launch with scalable cloud infrastructure for rapid performance and easy access from any location.
This approach ensures your software evolves with your business rather than limits it.
The Bottom Line: Custom load planning software is ideal for businesses with unique workflows, integration needs, or scaling goals. It offers long-term flexibility and control that off-the-shelf tools often lack.
Step-by-Step Load Planning Software Development Process
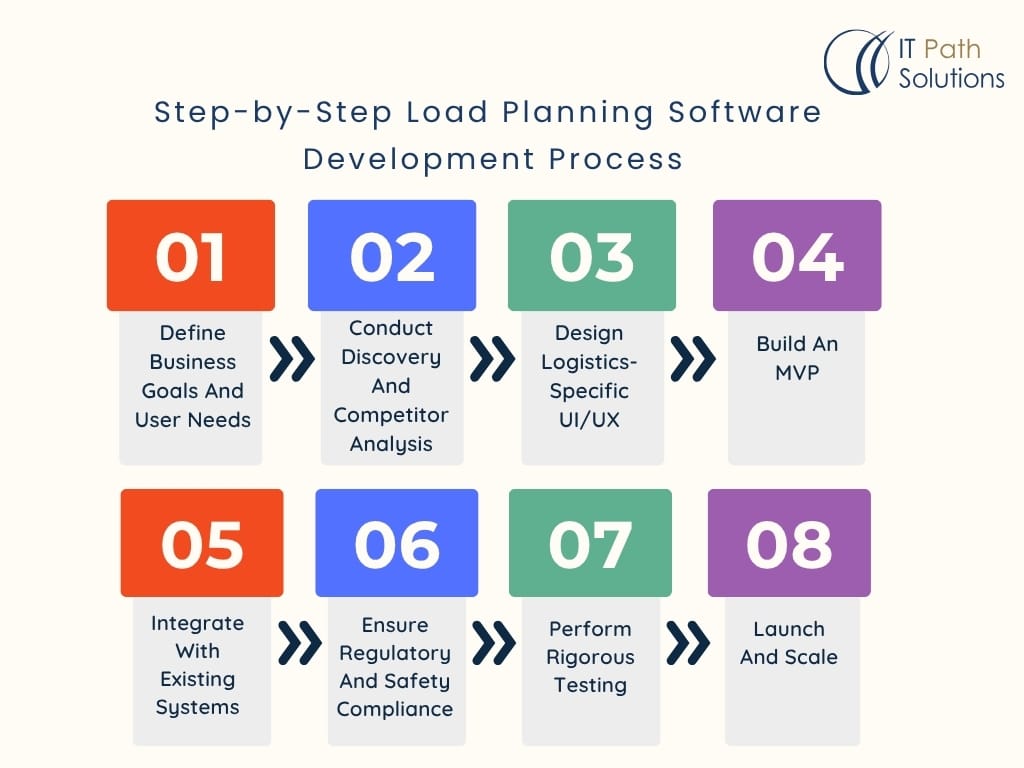
Building a powerful load planner software requires more than writing code. It’s about creating a solution that understands how freight moves, what regulations matter, and how logistics teams think. Here’s how the development journey unfolds from concept to launch.
Step 1: Define Business Goals And User Needs
Begin with clarity. What problem will your software solve? Whether it’s truckload planning for regional carriers or 3D cargo modeling for aircraft load planning software, align features with user expectations and business outcomes.
Step 2: Conduct Discovery And Competitor Analysis
Understand the gaps in existing load optimization software. Study how leading transportation management software or shipping logistics software handles routing, cargo validation, and integration. This step helps develop a more focused and competitive product.
Step 3: Design Logistics-Specific UI/UX
Intuitive design is key. The interface must simplify complex load plans. Think drag-and-drop cargo placement, real-time dimension adjustments, and vehicle configuration tools that even warehouse staff can navigate with ease.
Step 4: Build An MVP
Start lean. Prioritize must-have features like load validation, vehicle matching, and compliance alerts. MVP development reduces time-to-market while allowing feedback-driven refinements.
Step 5: Integrate With Existing Systems
Ensure seamless integration with ERP, TMS, WMS, and route optimization software. Use APIs that support two-way syncing with carrier platforms, GPS, and fleet management software for maximum efficiency.
Step 6: Ensure Regulatory And Safety Compliance
Whether you’re dealing with international freight planning software or US trucking, build tools that help users adhere to regional and global regulations. Include alerts for weight restrictions, hazardous goods handling, and stacking rules.
Step 7: Perform Rigorous Testing
Simulate real-world logistics workflows to validate how your load planner software performs under different cargo types, transport modes, and use cases.
Step 8: Launch And Scale
Deploy the MVP, monitor performance, gather feedback, and roll out updates. Scale features as your customer base grows, from small carriers to enterprise-level logistics software development.
Core Insight: A structured development process ensures your load planning software is functional, compliant, and ready to evolve within real logistics environments.
How To Test Load Planning Software For Accuracy And Performance
A load planning tool is only as potent as its ability to handle the complexity of real-world logistics. Testing goes far beyond just fixing bugs. It validates whether the software can manage edge cases, optimize cargo correctly, and integrate seamlessly with your existing tech stack.
Here’s how to make sure your solution holds up under pressure.
Simulation Scenarios Across Shipping Types
Replicate real shipping scenarios, including full truckloads, mixed pallets, and odd-shaped cargo. Use varying vehicle types and loading patterns for trucking.
Test for weight balance and compartment constraints for aircraft load planning software. Scrutinizing by simulation mimics operational complexity and helps identify flaws early.
Virtual Load Validation And Compliance Testing
Run automated checks for overloading, axle weight distribution, stacking orders, and hazardous goods compliance. Ensure the load abides by DOT, FAA, or EU regulations, depending on the transport mode. It is pivotal to test against regulatory data sets regularly.
Route-Based Load Testing
When integrated with route optimization software, simulate different loading scenarios based on changing routes, delivery windows, and traffic data. It validates whether your system makes wise trade-offs between space, fuel, and time.
Stress Testing And Performance Benchmarking
Push the system beyond normal usage to find limits. Imitate hundreds of loads per minute or simultaneous multi-location use for enterprise logistics networks. Make sure cloud-based systems scale without lag.
Edge Case And Fallback Handling
Test with missing data, partially correct inputs, incompatible cargo types, or last-minute order changes. An excellent load planning software always provides fallback options or suggestions instead of crashing.
Knowledge Drop: Testing must go beyond bug fixing. It should prove the software’s ability to optimize loads, adapt to dynamic logistics conditions, and comply with regulations under pressure.
Best Practices For Load Planning Software Development
Building load planning software is not just about writing code. It is about designing a logistics engine that delivers speed, accuracy, and flexibility to supply chain professionals.
The following best practices will help you develop a product that works exceptionally from day one and continues to perform at scale.
Prioritize Data Accuracy And Standardization
Your load planner software must process structured, unstructured, and often inconsistent data. Standardize inputs like cargo dimensions, vehicle specs, and shipment IDs to reduce errors during planning. Filtered and organized data leads to more insightful load decisions and safer transport execution.
Choose The Right Tech Stack And APIs
Select a tech stack that can evolve with your business needs. Lightweight front-end frameworks, powerful optimization engines, and reliable APIs for ERP, GPS, and TMS integration are vital. Prioritize open architecture that supports third-party tools without custom rewrites.
Build With Edge Cases In Mind
Your software must handle the unexpected, from irregular cargo shapes to sudden route changes. Designing for exceptions, not just the ideal case makes your system more valuable to real-world users.
Create Logistics-Centric UI And UX
The best load planning tools are built for planners, not engineers. Use intuitive drag-and-drop features, visual cargo placement, and color-coded validation cues. Reduce manual data entry and clicks to boost speed and usability.
Emphasize Security And Compliance
Your platform may store sensitive data, including shipping manifests, personal details, and regulatory certifications. Encrypt data both at rest and in transit. Stay compliant with regional and international safety and privacy standards.
Plan For Future Integrations
Whether it is connecting to new warehouse systems or switching fleet management software, your platform should allow future expansion without costly rebuilds. Modular design ensures flexibility as your logistics ecosystem grows.
Must-Know Insight: Smart architecture, clutter-free data, edge-case planning, and logistics-first design are the cornerstones of effective load planning software that performs reliably in the real world.
Cloud-Based Load Planning Software: Why It’s The Future
The logistics industry is moving faster than ever. Real-time data, growth-friendly infrastructure, and mobile-first access are expected. Hence, cloud-based load planning software is becoming the standard for businesses looking to stay competitive in 2025.
Cloud vs. On-Premise: A Clear Shift
On-premise systems offer total control but come with substantial infrastructure costs and limited scalability. In contrast, cloud-based platforms are flexible, easier to maintain, and allow teams to work across regions without a local install.
You can access your load planning environment from anywhere, whether at a warehouse or on the road.
| Feature | Cloud-Based Software | On-Premise Software |
| Deployment Time | Quick and remote | Slower, needs manual setup |
| Accessibility | Access anywhere via browser or app | Limited to installed devices |
| Maintenance and Updates | Automatic and vendor-managed | Manual and IT-dependent |
| Cost Structure | Subscription-based | High upfront cost plus hardware expenses |
| Scalability | Easy to scale with demand | Scaling requires more hardware |
| Integration Flexibility | Better API and third-party tool support | Often rigid and less integrative |
| Ideal For | Enterprises with distributed operations | Companies with strong internal IT teams |
Why Cloud Is The Smart Choice For Load Planning
A cloud-first approach ensures your planners, drivers, and warehouse staff can view and update load plans in real-time. This flexibility reduces decision delays, improves coordination, and helps optimize loads using the latest data.
Cloud platforms also enable better collaboration with carriers, suppliers, and customers without additional software layers.
Enterprise Benefits Of Going Cloud
Enterprises managing large fleets and multiple warehouses benefit the most from cloud migration. The cloud-native architecture ensures high availability, disaster recovery, and global syncing of routes, vehicle assignments, and load configurations.
Additionally, mobile access empowers frontline teams to review or update plans on the go.
The Crux: Cloud-based load planning software enables speed, scale, and real-time collaboration, making it an excellent choice for logistics companies operating in an increasingly connected and mobile-first world.
How To Implement Load Planning Software In Existing Systems
Even the most powerful load planning software cannot deliver results if it is integrated incorrectly. Implementation is not just about installing a tool; it is about ensuring that your load planning solution communicates effectively with the systems you already depend on. That includes everything from your ERP to your TMS, WMS, GPS tracking tools, and fleet management platforms.
Step-by-Step Implementation Strategy
A successful rollout of load planning software begins with thoughtful planning and stakeholder alignment.
Step 1: Define Integration Objectives Clearly
Start by mapping what your load planning software needs to communicate with, such as ERP for order data, WMS for inventory locations, GPS for real-time tracking, or carrier APIs for booking. Clarify what you want to achieve with each connection.
Step 2: Set Up API-Based Integration
Use secure APIs to ensure seamless data exchange across systems. REST or GraphQL APIs are commonly supported by modern transportation and logistics software platforms. It makes syncing shipments, vehicles, and route plans more dynamic and trustworthy.
Step 3: Build A Centralized Data Flow Architecture
Establish a data flow where all systems update in real-time without manual input. Your load planning software should pull shipment and vehicle data automatically and push optimized plans back into dispatch or warehouse systems.
Step 4: Train The Staff For Usage And Collaboration
Implementation is only successful when your team knows how to use the system. Offer hands-on training sessions for logistics managers, dispatchers, and warehouse staff. Focus on how the tool improves their day-to-day tasks, such as reducing errors or accelerating loading times.
Step 5: Test Integration Before Full Launch
Before going live, simulate various loading scenarios with test data. Make sure shipments from your ERP flow smoothly into your load planning system, that plans sync with route optimization software, and that updates reflect instantly on the dispatch dashboard.
Tools And Systems Commonly Integrated
| System Type | Integration Purpose |
| ERP (e.g., SAP, Oracle) | Shipment orders, billing, and inventory sync |
| WMS (Warehouse Management) | Inventory locations and dock scheduling |
| TMS (Transportation Management) | Carrier selection and dispatch automation |
| GPS and Fleet Tracking | Real-time vehicle location and ETA updates |
| Route Optimization Software | Aligning loads with the most efficient delivery paths |
| Carrier APIs (FedEx, DHL, etc.) | Auto-booking shipments and tracking through third-party carriers |
Main Point: Smooth integration of load planning software with your existing logistics stack ensures real-time data flow, informed decision-making, and streamlined operations across warehouses, fleets, and dispatch teams.
Load Planning Software Pricing And Cost Estimate
The cost of developing or implementing load planning software can vary widely depending on your needs, goals, and system complexity. Whether you’re building a custom solution or choosing a ready-made platform, it’s pivotal to understand where your investment goes.
Factors That Influence The Cost Of Load Planning Software
Several key components shape your final budget:
Features And Functionality
Basic features like load calculation, vehicle matching, and drag-and-drop interfaces are more affordable. Costs increase with advanced capabilities such as 3D visualization, AI optimization, real-time GPS syncing, and mobile access.
Deployment Type
Cloud-based load planning software often follows a subscription pricing model, which can be more budget-friendly upfront. On-premise solutions require a larger initial investment but may offer more control and customization.
Custom Development Scope
If you’re opting for custom load planning software development, the price will depend on design complexity, backend architecture, third-party integrations, and the number of supported users or devices.
Integration With ERP, TMS, WMS, And GPS Systems
Integrating load planning software with your existing systems may require API development, custom middleware, and testing. Each adds to the overall cost.
Ongoing Maintenance And Support
Plan for long-term support, updates, and feature enhancements, irrespective of whether you’re building or buying.
Load Planning Software Cost Breakdown
| Type | Estimated Cost Range | Notes |
| Off-the-shelf Software (Basic) | $5,000 to $25,000 annually | SaaS plans, good for small businesses |
| Off-the-shelf (Enterprise Tier) | $30,000 to $100,000+ annually | Includes advanced features and support |
| Custom MVP Development | $40,000 to $70,000 (one-time) | Basic version with core features |
| Full Custom Solution | $100,000 to $250,000+ | Includes advanced features, integrations, and UI |
| Integration & API Development | $10,000 to $50,000 | Depending on the number and complexity of systems |
| Post-Launch Support & Maintenance | $2,000 to $10,000 monthly | Varies by SLAs and scale |
➡️ Note: Pricing may vary based on geography, development partner, and scope.
MVP vs. Full Solution: Where To Start?
Launching with a minimum viable product (MVP) is the most intelligent move for many businesses. You validate your idea, collect feedback, and optimize before scaling. A well-built MVP can cover 70 to 80 percent of your immediate load planning needs and evolve based on real usage data.
Key Takeaway: The cost of load planning software depends on features, integration needs, and whether you develop or purchase. Start with a smart MVP to manage expenses while gaining early ROI.
Selecting The Best Load Planning Software Solution Provider
Finding the ideal load planning software development company or vendor is one of the most critical decisions in your entire project journey. It can determine how smoothly the software integrates into your logistics workflow and whether it supports your long-term growth.
Whether you’re looking for custom load planning solutions or evaluating off-the-shelf tools, selecting a partner with extensive logistics experience is crucial.
What To Look For In Vendors And Development Services
Domain Expertise
A provider with hands-on experience in logistics, fleet management, or transportation software will understand your challenges and recommend relevant features out of the box.
Proven Portfolio And Case Studies
Look for companies that have built or worked on load planner software, freight optimization tools, or transportation management software. Their work should be visible through detailed case studies, not just vague claims.
End-to-End Capabilities
From UI/UX design personalized for logistics operators to backend systems that handle real-time updates and compliance checks, the vendor should offer complete product development, not just coding.
Scalable Architecture And Integration Expertise
Your software should integrate smoothly with ERP, WMS, GPS tracking, and third-party APIs. Seek teams with vast experience in systems architecture, data syncing, and scaling applications across locations.
Transparent Communication And Agile Delivery
You need a partner who is clear about timelines, risks, and pricing. Agile methodology, sprint-based releases, and regular demos help keep your project on track.
Custom vs. Off-the-Shelf Load Planning Software Vendors
| Criteria | Custom Software Vendor | Off-the-Shelf Vendor |
| Fit to Business Requirements | Tailored to exact needs | May require process adjustments |
| Time to Deploy | 4–8 months (varies by scope) | Immediate to 2 weeks |
| Scalability | Built with future scale in mind | May hit limits as operations grow |
| Initial Investment | High upfront, long-term ROI | Lower cost but recurring fees |
| Flexibility | Fully customizable | Limited configuration options |
| Integration Capability | Built to connect with your existing tools | Varies by vendor and edition |
Red Flags To Watch Out For
- Imprecise answers about logistics use cases
- Lack of integration knowledge with TMS, ERP, or GPS
- No defined QA or testing approach
- Cookie-cutter pricing without discovery
- Teams that outsource development without disclosure
What This Means For You: Choose a load planning software provider who understands logistics inside and out, offers end-to-end support, and builds scalable, integration-ready solutions tailored to your goals.
Scaling Load Planning Software For Growing Logistics Networks
Building a solid foundation is only the beginning. As your logistics operation expands across cities, regions, or countries, your load planning software must scale with it. Whether you operate five trucks or five hundred, the ability to adapt quickly without breaking your system is non-negotiable.
Scaling is not just about handling more data. It means improving performance, ensuring accuracy under load, and supporting users across departments, warehouses, or geographies.
How To Scale Load Planning Software Across Multiple Locations
Multi-Location Support
Your software should allow warehouse and fleet managers in different hubs to access the same data in real-time, customize settings for each region, and sync updates without conflicts.
Role-Based Access And User Management
As more teams use the software, control who can view, edit, or export data. Set permissions based on departments, regions, or job roles.
Load Balancing And Server Optimization
If you’re working with a cloud-based solution, ensure your infrastructure is designed to handle spikes in traffic, seasonal surges, or cross-country operations.
Modular Architecture For Feature Upgrades
Future-ready software should be built with a modular design. That way, you can add new features like real-time tracking or carbon emission calculators without overhauling your entire system.
Performance Optimization Tips
- Use asynchronous data processing for real-time load planning
- Optimize database queries to reduce latency in plan generation
- Implement caching for frequently used vehicle or cargo templates
- Select a tech stack built for scale, such as Node.js, Go, or Java, with microservices
Planning For Growth: From Regional To Enterprise Use
Think about how your software needs may change when you go from 10 shipments a day to 1,000. Start with a flexible data model that supports:
- Multiple warehouses and vehicle types
- International compliance standards
- Time zone and currency support
- Real-time dashboards with aggregated insights
Essential Insight: Scalability means building load planning software that performs well across locations, teams, and shipment volumes while keeping data accurate, secure, and actionable at every level.
Load Planning Software For Compliance And Safety Standards
In logistics, safety is more than a checkbox. It’s a regulatory requirement, a business priority, and a brand promise. Whether you’re operating across state lines or international borders, load planning software helps you stay compliant with current and evolving standards.
Industry Regulations To Watch
- FMCSA (Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration): Enforces weight limits, axle load restrictions, and driver hours of service in the US.
- DOT (Department of Transportation): Requires secure cargo, vehicle inspections, and proper load distribution.
- EU Directives and ELD Mandates: European freight carriers and cross-border transport must comply with region-specific digital logging and load limits.
- IATA for Air Cargo: Aircraft load planning software must align with weight distribution and cargo restraint regulations for flight safety.
Compliance Features That Matter In 2025
Axle Load And Weight Limit Monitoring
Automatically calculate total vehicle weight and axle-wise distribution to prevent overloading.
Real-Time Safety Alerts
Flag non-compliant loads during planning and suggest corrective actions instantly.
Digital Audit Trails
Maintain logs of who created, approved, or modified a load plan. It is crucial for audits and insurance purposes.
Secure Load Modeling
Simulate and validate container stability, load sequencing, and tie-down points to ensure safe transportation.
Global Standards Database
Keep your software updated with changing local, national, and international logistics laws.
Why Compliance-First Design Matters
Compliance lapses can result in fines, vehicle downtime, or worse – accidents. Designing your load planner software with regulatory frameworks in mind lowers risk and strengthens your brand’s credibility in competitive logistics networks.
Final Thought: Compliant load planning software doesn’t just protect against penalties; it ensures safe, legal, and systematic cargo movement across regions and industries.
Conclusion
In a world where efficiency defines competitive edge, load planning software has moved from being a helpful tool to an operational necessity. From reducing transportation costs to improving cargo safety and regulatory compliance, it plays a pivotal role in how modern logistics, manufacturing, and trucking companies operate.
This guide has taken you through everything you need to know about building load planning software in 2025. We’ve explored what the software does, who needs it, how it works, and why the cloud, AI, and integration capabilities are now non-negotiables.
You’ve also seen what it takes to design, develop, test, scale, and maintain this kind of system, whether for a small logistics team or an enterprise fleet.
Remember, success starts with strategic thinking, the right technology stack, and a development partner who understands logistics as well as comprehends code. It doesn’t matter if you plan to build a custom solution or choose a load planning software development partner who knows this space inside out.
The future of logistics is savvy, compliant, and customer-focused. So, start your journey today by developing a load planning solution that not only meets industry standards but sets new ones.
FAQ
How Long Does It Take To Build Load Planning Software From Scratch?
The average timeline ranges from 4 to 9 months, depending on feature complexity, integrations, and team size. Building a robust MVP may take 10 to 14 weeks. However, scaling it into a full-fledged solution can extend the timeline substantially.
Can Load Planning Software Be Integrated With Legacy Logistics Systems?
Yes, custom APIs and middleware tools allow integration with older systems. However, legacy compatibility may require additional time and budget, especially for outdated ERP or WMS platforms that lack modern API support.
What Programming Languages Are Commonly Used For Load Planning Software?
Typical choices include Python for algorithms, JavaScript (React or Angular) for front-end interfaces, and Node.js or Java for backend logic. You can also use cloud-native tools like AWS Lambda or Firebase for scalability.
Is It Possible To Add AI Features To An Existing Load Planning Tool?
Yes, AI modules can be integrated into existing tools for tasks like predictive loading, demand forecasting, or automated route suggestions. It typically requires retraining the model using your operational data.
What Kind Of Post-Launch Support Is Needed For Load Planning Software?
Post-launch support should include system monitoring, bug fixes, security patches, periodic performance tuning, and updates for regulatory compliance. Many companies also opt for SLA-based ongoing support contracts with their development partner.
What Are The Benefits Of Cloud-Based Load Planning Software?
This question is timely and taps directly into buyer intent, especially as businesses compare cloud vs on-premise options. It also helps reinforce scalability, remote access, and real-time data sync, making it ideal for SEO and user engagement.
Which Industries Benefit Most From Load Planning And Optimization Software?
The software is excellent for expanding reach to specific niches (trucking, manufacturing, air cargo, etc.). It can also help drive relevant traffic from users looking to validate whether such tools apply to their domain.
What Is the ROI of Investing in Enterprise Load Planning Software?
Enterprise load planning software generally delivers ROI through reduced transportation costs, better asset utilization, fewer loading errors, and faster planning cycles.
Companies often experience measurable savings within months due to automation, real-time insights, and improved efficiency across logistics and supply chain operations.

Keyur Patel
Co-Founder
Keyur Patel is the director at IT Path Solutions, where he helps businesses develop scalable applications. With his extensive experience and visionary approach, he leads the team to create futuristic solutions. Keyur Patel has exceptional leadership skills and technical expertise in Node.js, .Net, React.js, AI/ML, and PHP frameworks. His dedication to driving digital transformation makes him an invaluable asset to the company.
Related Blog Posts

Top 7 Custom Software Development Challenges (and How to Overcome Them in 2026)
Think like this. It is Q3 of 2025. You are a CTO or a Product Manager. You have just secured the budget for a new enterprise platform that promises to revolutionize your supply chain. You hire a software development company, sign the contracts, and the kickoff meeting feels perfect. Everyone is nodding. Everyone gets it.… Top 7 Custom Software Development Challenges (and How to Overcome Them in 2026)

Mastering Software Maintenance In 2025: Costs, Strategy, Tools, And More
Software is never truly finished. The moment it goes live, the real work begins. No matter how carefully it’s developed, an application cannot remain functional, secure, and competitive without continuous upkeep. Imagine launching a sleek, high-performing app only to see it slowly break down due to hidden bugs, compatibility issues, or outdated compliance requirements. That… Mastering Software Maintenance In 2025: Costs, Strategy, Tools, And More
Best DevOps Tools For Automation & Scalability In 2025
Have you ever asked yourself, “Are we using the best tools for scalability, automation, and growth, or just the most popular ones that don’t truly serve our business?” That single question can determine how fast you ship, how stable your systems are, and how well your team performs. It is also a significant difference that… Best DevOps Tools For Automation & Scalability In 2025



