No-Code & Low-Code Platforms: What They Mean for Traditional Developers
Keyur Patel
January 23, 2026
8 min
Software development has followed an ongoing path. They have followed it from decades. Business teams defined requirements. Developers translated those requirements into code. Releases were slow, careful and often constrained by time. Plus, budget and available engineering talent.
That model is changing.
No‑code platforms are reshaping how applications are built. Low‑code tools are changing who builds them. Ideas move faster into software when they work together. Website builders started out simple. Over time, they became powerful platforms. These tools can now be taken on enterprise workflows. Integrations are in their hands. Automation is something they handle with ease.
Engineering teams around the world are asking, “What do no-code and low-code platforms mean for traditional developers?”
Are they a threat? A shortcut? Or an opportunity?
It is not as simple as the headlines make it seem.
The Basics of No-Code & Low-Code Platforms

Let’s start by what these platforms are. After that, let’s then move to their impact.
What are No-Code Platforms?
No-code platforms allow users to build applications. They can do it without writing any code. Instead, they rely on visual interfaces. And even pre-built components.Configuration rules and workflows complete the process.
Users assemble applications by:
- Dragging and dropping UI components
- Defining logic through visual flows
- Connecting data sources using connectors
- Configuring rules instead of coding them
These platforms are designed primarily for non-technical users. They are often referred to as citizen developers.
What is Low-Code Development?
Low‑code development bridges the gap. The gap between traditional coding and no‑code tools. Developers still write code but far less than before.
Low-code platforms provide:
- Visual development environments
- Pre-built logic blocks
- Reusable templates and components
- Code extensions for custom logic
This approach accelerates rapid application development while still allowing professional developers to control architecture, performance and integrations.
Citizen Development finds its Moment
A major change with no-code platforms? It is citizen development. It is changing who builds applications.
Citizen developers are business users. They include product managers, operations teams, analysts and marketers. These users create applications themselves. They do it to solve specific problems. And they do not rely entirely on engineering teams.
Internal tools. Dashboards. Workflows. They keep piling up. Reporting systems and automation requests add to the demand. They grow faster than engineering teams can deliver them. No‑code platforms fill that gap. The tools let teams deliver on demand.
For organizations, this means:
- Faster problem solving
- Reduced dependency on IT backlogs
- Greater flexibility in operations
For developers, it changes their role. And so does the way they connect to the bigger ecosystem.
Low-Code Tools Impact on Traditional Development

The impact of low-code tools is often misunderstood as a replacement. But infact, it is more accurate to describe it as a redistribution of effort.
What Low-Code Replaces
Low-code development reduces the need for developers to spend time on:
- Repetitive CRUD applications
- Basic internal tools
- Simple approval workflows
- Standard dashboards
- Form-based data entry systems
These tasks are important. But they are not where developers deliver the most strategic value.
What Low-Code does not Replace
Low-code tools struggle or fall short when it comes to:
- Complex system architecture
- High-performance applications
- Custom algorithms and logic
- Advanced security requirements
- High‑volume consumer platforms
- Deep system integrations
- Legacy modernization at scale
These areas still require traditional developers with deep technical expertise.
The New Face of Development
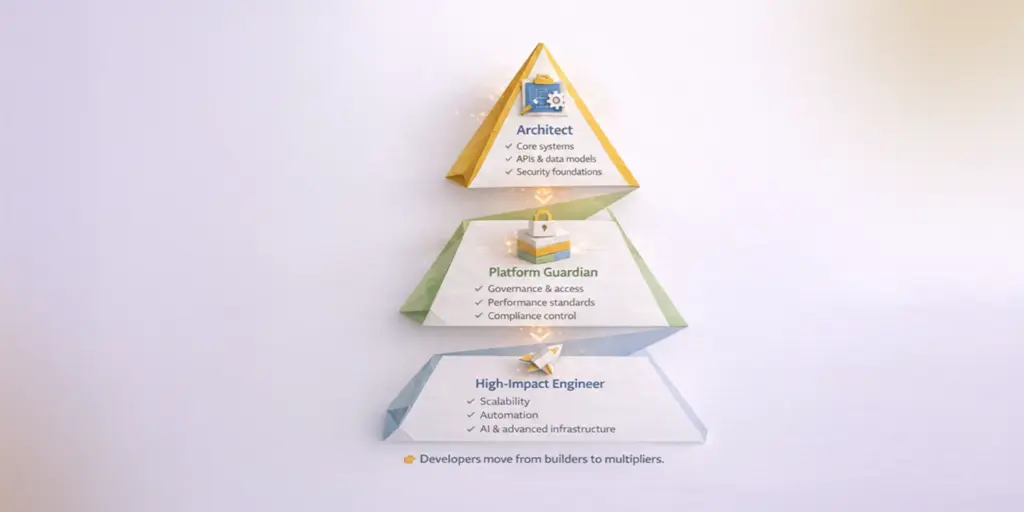
No‑code and low‑code do not take developers away. They simply change what developers work on.
1. Developers become System Architects
Traditional developers design core architectures. They also build APIs. Data models are part of their work. Security foundations come from them too. All of this enables no‑code platforms to work reliably and scale smoothly. It makes sure that business‑built applications do not break systems.
As citizen developers build surface-level applications, traditional developers increasingly design:
- Core architectures
- API layers
- Data models
- Security frameworks
- Integration standards
Developers define the foundations that no-code tools consume.
2. Developers Lead the Platform Change
Security is ensured through developer oversight. Performance remains consistent under their guidance. Compliance is built into the framework. Consistency is maintained across systems. Rules, access controls and standards provide the foundation. This keeps rapid low‑code development stable and maintainable. And even free from long‑term technical debt.
Low-code tools introduce governance challenges:
- Data access control
- Security compliance
- Performance consistency
- Versioning and lifecycle management
Developers now act as:
- Platform owners
- Technical gatekeepers
- Quality enforcers
- Integration specialists
This makes sure that rapid application development does not create long-term technical debt.
3. Developers focus on High-Impact Engineering
Freed from basic builds, developers shift their focus. Scalability becomes a priority. Performance and security demand attention. Automation and stronger infrastructure take center stage. This work drives business growth and keeps complex systems reliable under scale.
With basic applications handled elsewhere, developers can invest time in:
- Scalability improvements
- Performance optimization
- Security hardening
- Advanced analytics
- AI + automation
- Stronger infrastructure
This elevates the role of developers. It does so instead of reducing them to a commodity.
No-Code and Low-Code Platforms Advantages
These platforms create measurable business and technical benefits. This is possible only when used correctly.
Faster Time to Market
Low-code development cuts build cycles down. Applications that once took months to build are now much faster. They can be deployed in weeks or even days.
This speed is critical for:
- MVP validation
- Internal process automation
- Rapid experimentation
- Short-term market opportunities
Reduced Engineering Bottlenecks
No-code platforms free engineering teams from constant minor requests. Developers are not buried in small tasks anymore. Their energy goes to work that needs them.
Improved Collaboration between Business and Tech
Visual tools bridge the communication gap between business teams and developers. Requirements become tangible prototypes instead of abstract documents.
This reduces:
- Misinterpretation
- Rework
- Long feedback loops
Scalable Innovation
Low-code platforms enable organizations to test ideas. They do it cheaply and quickly. Full-scale development comes only after validation.
The Hidden Risks Developers should be Aware of
Even if they have their benefits, no-code and low-code platforms are not risk-free.
Shadow IT and Fragmentation
Without proper governance, citizen development can lead to:
- Duplicate applications
- Inconsistent data sources
- Security vulnerabilities
- Poor maintainability
Developers play a critical role in preventing this. It is by defining standards and controls.
Vendor Lock-In
Many no-code platforms are proprietary. Migrating away later can be difficult or costly.
Traditional developers must evaluate:
- Data portability
- API accessibility
- Custom extension support
- Long-term viability
Performance and Scalability Limits
No-code tools work well for defined use cases. But often struggle at scale. Applications built quickly may not handle high concurrency or complex logic efficiently.
This is the point where low‑code stops. And traditional development begins.
No-Code. Low-Code. Traditional Development
Rather than competing approaches, these models work best together.
| Use Case | Best Fit |
| Simple internal tools | No-Code Platforms |
| Workflow automation | Low-Code Development |
| Rapid prototypes | Low-Code |
| Customer-facing apps | Traditional Development |
| High-performance systems | Traditional Development |
| Enterprise platforms | Hybrid approach |
The Irreplaceable Role of Traditional Developers
Even with automation and visual tools, software isn’t getting simpler. Its complexity keeps growing.
Consider what still depends on traditional developers:
- Designing systems that handle growth smoothly
- Making sure user data stays secure
- Keeping operations aligned with regulations
- Building reliable integrations
- Managing cloud infrastructure
- Optimizing performance under load
No-code platforms build on top of these foundations. They do not replace them. In fact, the more organizations adopt no-code tools… the more they need skilled developers to:
- Set boundaries
- Build extensibility
- Maintain system integrity
The Future lies in Collaboration
The future of development is not no-code versus developers. It is no-code with developers.
- Successful teams treat no-code platforms as:
- Accelerators, not shortcuts
- Extensions, not replacements
- Business enablers, not architecture owners
Traditional developers who adapt to this reality gain leverage. They spend less time building forms. And they spend more time solving complex problems.
Path to What comes Next
No‑code and low‑code are changing software. They shift who is doing the building. And they make organizations move quicker. Citizen development becomes possible. Applications can be built faster. Bottlenecks in delivery are reduced.
For developers, the shift is not something to fear. It is an opportunity to grow.
By embracing low‑code tools where they make sense, developers expand their impact. Architectural strength is preserved. Security stays in place. Performance continues to matter. Developers become more strategic.
Software demand is climbing fast. The most valuable developers are not the ones cranking out the most code. The most valuable developers will design scalable systems. Those systems will adapt over time. And they will let others build safely on top.
And that future still needs developers. Perhaps more than ever.
Questions that keep arising
- Will no-code and low-code platforms replace traditional developers?
No. No-code platforms reduce repetitive work. But traditional developers are essential for architecture and security. They ensure integration and scalability. They govern the systems that no‑code tools depend on.
- What is citizen development and why does it matter?
Citizen development allows non-technical teams to build applications. It is by using low-code tools. It matters because it speeds up delivery. But it still requires developer oversight to avoid security and scalability issues.
- When should businesses avoid no-code or low-code platforms?
No‑code and low‑code are not right for complex systems. They are not suited for performance‑critical applications. They struggle with deep customization. Traditional development keeps things stable and under control.

Keyur Patel
Co-Founder
Keyur Patel is the director at IT Path Solutions, where he helps businesses develop scalable applications. With his extensive experience and visionary approach, he leads the team to create futuristic solutions. Keyur Patel has exceptional leadership skills and technical expertise in Node.js, .Net, React.js, AI/ML, and PHP frameworks. His dedication to driving digital transformation makes him an invaluable asset to the company.
Related Blog Posts

WordCamp Canada 2025: Insights from Bhumi at IT Path Solutions
Last week, our team at IT Path Solutions was thrilled to have Bhumi attend WordCamp Canada 2025. The event offered an incredible opportunity to connect with the WordPress community, learn from experts, and gather insights that help us serve our clients even better. Learning and Inspiration Bhumi attended sessions covering a wide range of topics… WordCamp Canada 2025: Insights from Bhumi at IT Path Solutions

Dynamic Pricing For Transportation Apps: How Zone-Based Pricing Maximizes Revenue
Imagine hailing a ride during rush hour, only to see the fare triple within minutes. At first, it feels unfair. But here’s the twist: that substantial shift in price is what keeps drivers on the road, passengers moving, and platforms profitable. Without intelligent pricing, transportation apps would collapse under the weight of mismatched supply and… Dynamic Pricing For Transportation Apps: How Zone-Based Pricing Maximizes Revenue

.NET MAUI Development in 2025: The Complete Guide with Real-World Developer Insights
Your team launches a new Android app. Weeks later, the iOS version remains in testing while desktop users wait indefinitely. Deadlines slip, budgets stretch, and developers struggle with duplicate code. This scenario plays out daily in development teams worldwide, but it doesn’t have to be your reality. Enter .NET MAUI: one codebase, four platforms (Android,… .NET MAUI Development in 2025: The Complete Guide with Real-World Developer Insights
